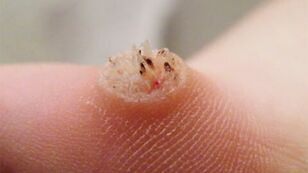
Warts are benign neoplasms of small aesthetics that appear on the skin when infected with the human papilloma virus. Entering the upper layers of the epidermis, the virus provokes the proliferation of its cells, which results in the appearance of warts of various shapes, sizes and colors.
The human papilloma virus infects about 80% of people on the planet, and not every patient knows about its diagnosis, because HPV is asymptomatic in most cases.
Types of warts
There are different types of warts, depending on the position on the body, color, size, shape and type of pathogen.
Common or vulgar warts
Most often, their appearance does not depend on the age or gender of the patient. They are located on the hands, between the fingers, on the back of the palms (rarely on the palms themselves). Vulgar warts are irregular or round in shape, and due to their fleshy-pink color, they are usually not too noticeable on the skin. The size varies from 1 to 3 mm, with prolonged infection and absence of treatment, groups of neoplasms may appear in the affected area.
Straight nipples
Neoplasms of this type are more common in children and adolescents, hence their other name is juvenile warts. These are nodules of body or light brown color, oval or round, smooth surface, slightly raised above the skin. Mainly localized on the skin of the face, neck, arms and upper body.
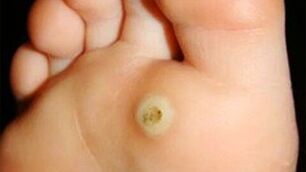
Plantar warts
This type of wart appears exclusively on the skin of the feet, which is why it got its name. It is a rough growth with a keratinized layer of skin or a group of such growths. The skin around the plantar warts loses its natural color and becomes gray-yellow. The surface of the nipple becomes hard and begins to press on the healthy tissue around it, causing serious discomfort.
Hanging nipples
The peculiarity of this species is the presence of narrow articulation with the surface of the skin, the so-called "legs". Hanging nipples can be oblong, round or irregular, pink or reddish in color. Such warts are localized on the neck, face, armpits, under the breast in women. Often the appearance of numerous drooping warts signals a sharp decrease in the body's immune status.
Senile warts
Warts of this type are more likely to affect the skin of older people. They are also called seborrheic warts or keratomas. They develop due to age-related changes and deterioration of metabolism from epidermal cells, often affecting the upper part of the hair follicles. Keratomas have a round shape, well-defined borders, are localized on the scalp or face. The size varies from a few millimeters to 4-5 cm.
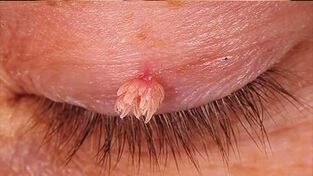
Genital warts
Genital warts or condyloma are the most uncomfortable and painful type of neoplasm. They are caused by human papilloma virus types 6 and 11. Genital warts affect the skin along the mucosa: on the lips and eyelids; in the area of the genitals, urethra, anus.
Genital warts have the structure of nodular growths that are often compared to cauliflower or rooster. Condyloma is connected to the surface of the skin by a thin “leg”. Due to localization in parts of the body that are susceptible to mechanical irritation, there is a high degree of injury to the genital warts and adjacent tissues, infection and the development of an inflammatory process with the formation of exudative or purulent discharge.
Causes of warts
Increased activity of human papilloma virus in the body provokes the appearance of warts. Infection occurs through contact and daily life: by touching, handling, common objects and in public places if personal hygiene is not respected. Genital warts are transmitted sexually.
A virus enters its active form if factors such as:
- severe or chronic stress;
- transmitted infectious diseases;
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal disorders, irregular metabolism;
- excessive sweating;
- trauma and microtrauma of the skin;
- in clothing and footwear made of unnatural materials.
If the disease is asymptomatic, it can only be diagnosed in the laboratory.
Warts in adults
Papillomas or warts can occur at any age. In this case, gender does not play a special role - both men and women are susceptible to HPV. At the same time, the risk of developing warts in women is higher, because their immunity is often weakened due to hormonal levels, pregnancy and feeding children. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, women are also more susceptible to the appearance of genital warts, especially genital warts, which increase the risk of developing cervical cancer.
In men, warts appear only in the case of a sudden decrease in immunity, which does not happen so often in the stronger sex. At the same time, men are extremely rarely carriers of HPV types 16 and 18, which provoke the development of oncological diseases.
Warts in children
Warts are common in children and adolescents because their immunity is not fully formed, as a result of which they are easily infected with papilloma viruses. An important role is played by the fact that children attending kindergartens and schools are usually in high stress conditions, which negatively affects the body's defenses. In addition to the household contact method, an intrauterine infection of the mother is also possible.
Children most often develop vulgar, juvenile or plantar warts, while young warts disappear on their own at the age of 14-18.
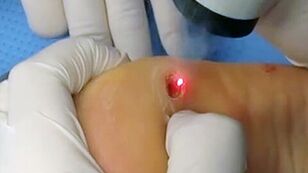
Warts Treatment
When treating warts, it should be understood that it is impossible to completely remove the pathogen from the body - the human papilloma virus. Once in the body, it remains in it forever, but a healthy immune system is able to keep it under control and minimize the manifestations of its vital activity.
The very fact of the appearance of warts indicates a decrease in the body's immune status, so measures to strengthen the immune system should be included in HPV therapy. With a reduced defensive reaction of the body, even with the successful removal of warts, there is a high probability of recurrence. However, in people with strong immunity, warts can disappear on their own.
Therapy should be selected by a competent physician after a thorough examination. Self-medication is unacceptable, because a layman will not be able to distinguish a wart from a malignant neoplasm. The issue of removingwartsis also decided by a specialist - an injured neoplasm can grow from benign to malignant.
There are the following ways to get rid of warts.
- Cryodestruction (freezing with liquid nitrogen). This method is especially effective for common warts. The neoplasm is exposed to liquid nitrogen for 10-30 seconds. This method is good for your little trauma; it takes 1 to 5 sessions for the wart to be completely removed.
- Laser coagulation (laser removal). The neoplasm is removed in parts under local anesthesia. A groove remains at the site of the nipple, which disappears after about a month.
- Electrocoagulation (removal by electricity). The wart is removed with a thin metal loop using high-frequency current. This method is characterized by the absence of bleeding and additional tissue disinfection. The tissues of the neoplasm remain intact, so they can be sent for histological examination. Traces of manipulation disappear within a week.
- Surgical excision. This method is used only in extreme cases, when the neoplasms are too large or are grouped into one conglomeration. Under local anesthesia, the wart is removed with a scalpel as in conventional surgery. The removed material is sent for histological examination. The presence of scars at the incision site depends on the skill of the surgeon applying the sutures.
- A chemical attack method that uses a variety of acids or alkalis. This method is the most painful, traumatic and most dangerous, because the risk of secondary tissue infection at the site of exposure is extremely high. When deciding on its use, it is worth bearing in mind that you can only act on the nipple itself, without affecting the skin nearby.
Warts medications
Topical medications are used to treat warts, but their effectiveness depends on the age of the neoplasm - the fresher the wart, the more likely it is that the patient's immunity will be removed.
Before using topical medications, you should consult a dermatologist and take tests to determine the nature of the neoplasm, as exposure to the medication can lead to nipple cell degeneration into malignancies.
Non-traditional methods of wart control
Use of traditional medicine recipes:
- garlic;
- bow; celandine;
- spurge;
- wormwood;
- linseed oil.
Traditional medicine is a good addition to the usual therapy after consulting a doctor.
Wart Prevention
The best prevention of warts is banal adherence to the rules of personal hygiene: timely hand washing, use of personal manicure accessories, towels, cloths, shoes. You should not go barefoot to the pool, shared showers, baths and saunas. Also, during your stay in hotels, it is worth taking antiseptics with you to treat bathrooms. In parallel, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system and take care of general health.























